3D CPM Simulation Results
Simulation Parameters:
- Each cell has a relaxed area of 27 lattice sites.
- Cells are initialized as
3x3x3cubes.
- Cells are initialized as
- Each simulation runs for 300 Monte Carlo (MC) time steps.
- Statistics in each case are gathered over 100 individual instances.
Mean Square Displacement (MSD)
\[d^2 = 4Dt^\alpha\]For normal diffusion \(\alpha = 1\) and \(D\) is the diffusion coefficient. As \(\alpha\) gets further away from 1 diffusion becomes anomalous and \(D\) is no longer the normal diffusion coefficient since it doesn’t have the units of \([\text{length}]^2 [ \text{time}]^{-1}\).
Results
Here are the results for groups of different sizes with the parameters listed above.
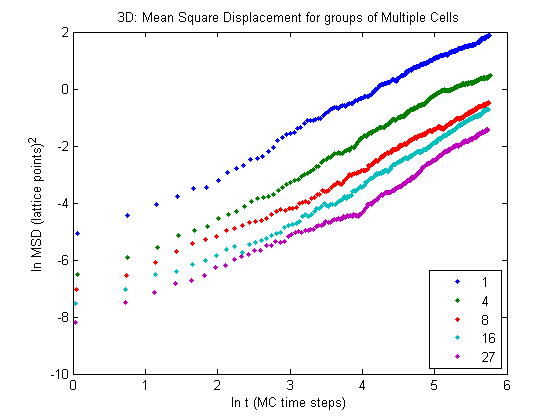
From the Szabo paper we know that cells should exhibit normal diffusion for times when the displacement is on (or above) the order of the size of the cells. This corresponds to times where \(\ln\text{MSD} \gtrsim 0\). We see that for most of the cases this criteria is not met within 300 MC time steps.
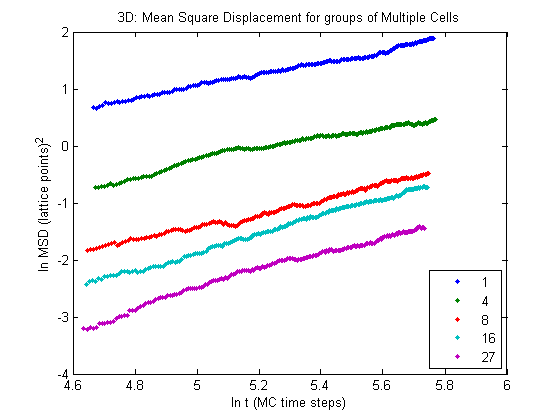
If we look at the last 200 MC time steps, we see that only cell groups of one and four cells meet this criteria. So we should expect normal diffusive behavior for those two cases and anomalous behavior for larger groups.
Fitting the data lets us calculate values for \(\alpha\) and \(D\).
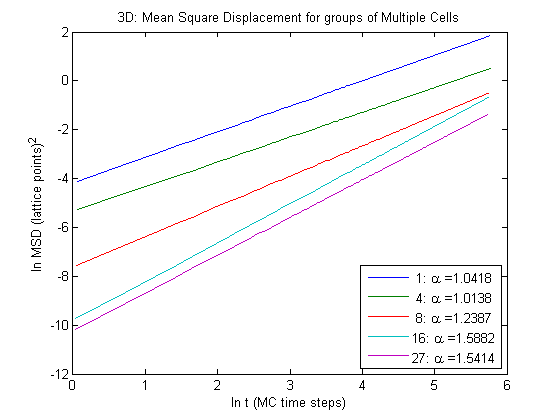
This is indeed what our results show. What is interesting to note is that the cell group experiences superdiffusion at scales that are smaller than a cell and much smaller than the whole group size. I suspect that if the simulations were left to run much longer such that large clusters’ MSD did pass the criteria then we would see normal diffusion at those times.
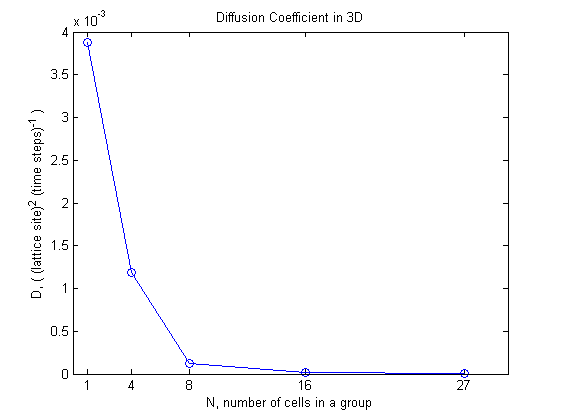
From the MSD plots we see that as group size increases the increase in MSD becomes slower and slower. This is reflected in the diffusion coefficient of each group. The diffusion coefficient dramatically decreases as group size increases.
Comparison Across Dimensions
Let’s examine how the diffusion coefficient as a function of group size varies across simulations of different dimensions.
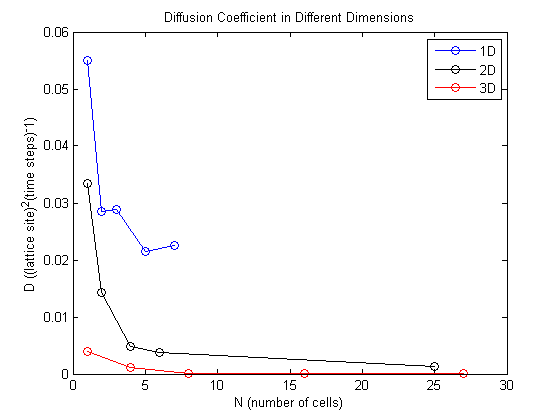
The general trend is that as we add dimensions the diffusion coefficient decreases. This makes sense since a particle moving in 3D will take significantly more time to explore the space around it than a particle restricted to motion in only one dimension.
It also should be noted that diffusion coefficients for 1D were obtained only for groups up to 7 cells because larger groups exhibited very anomalous diffusion.
3D Diffusion Movies
Here are a couple of movies displaying the type of behavior the groups of cells exhibit.
####1 Cell with a relaxed area of 27 lattice sites
####8 cell Group with individual relaxed area of 8 lattice sites
Written with StackEdit.
